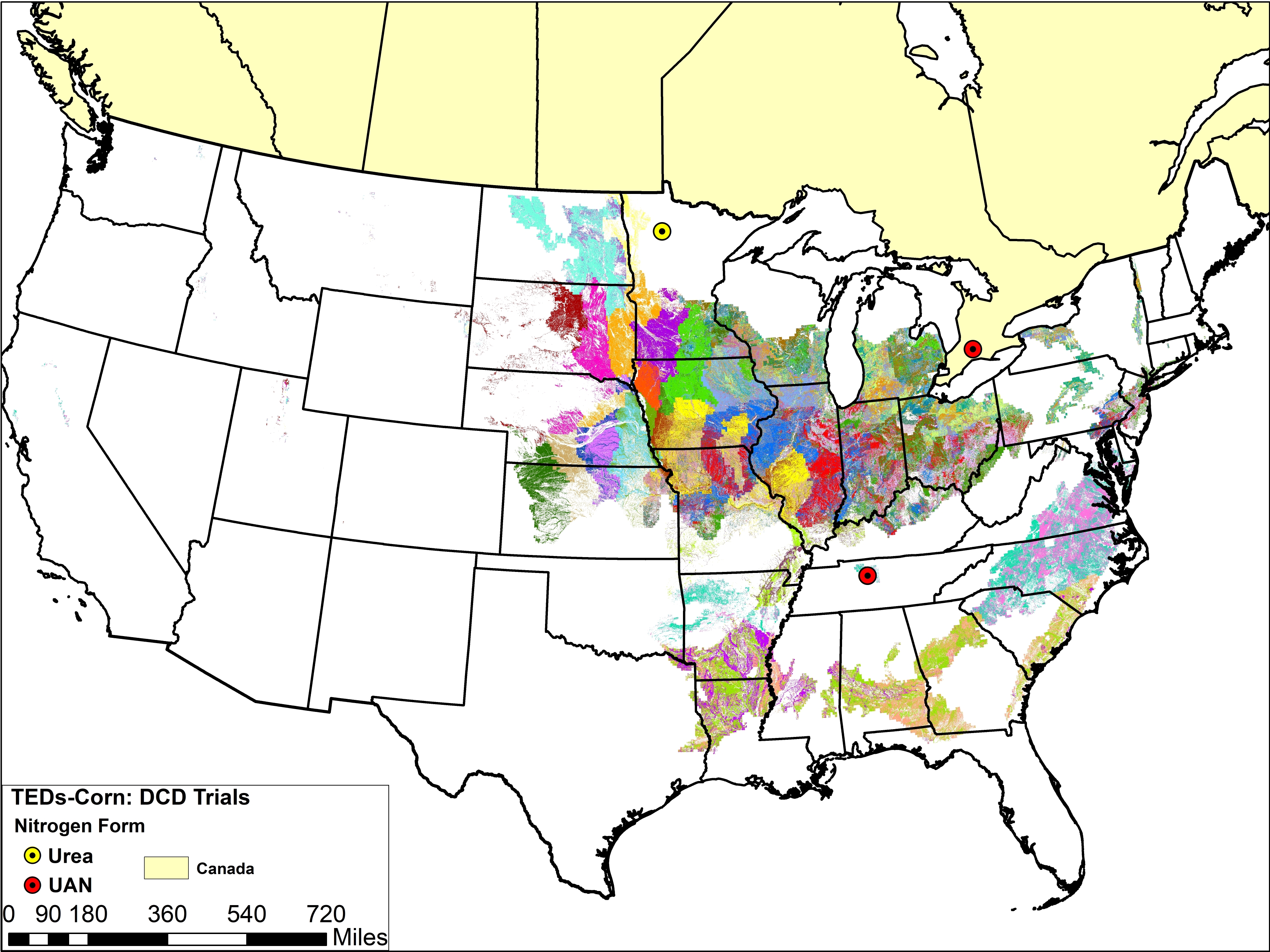
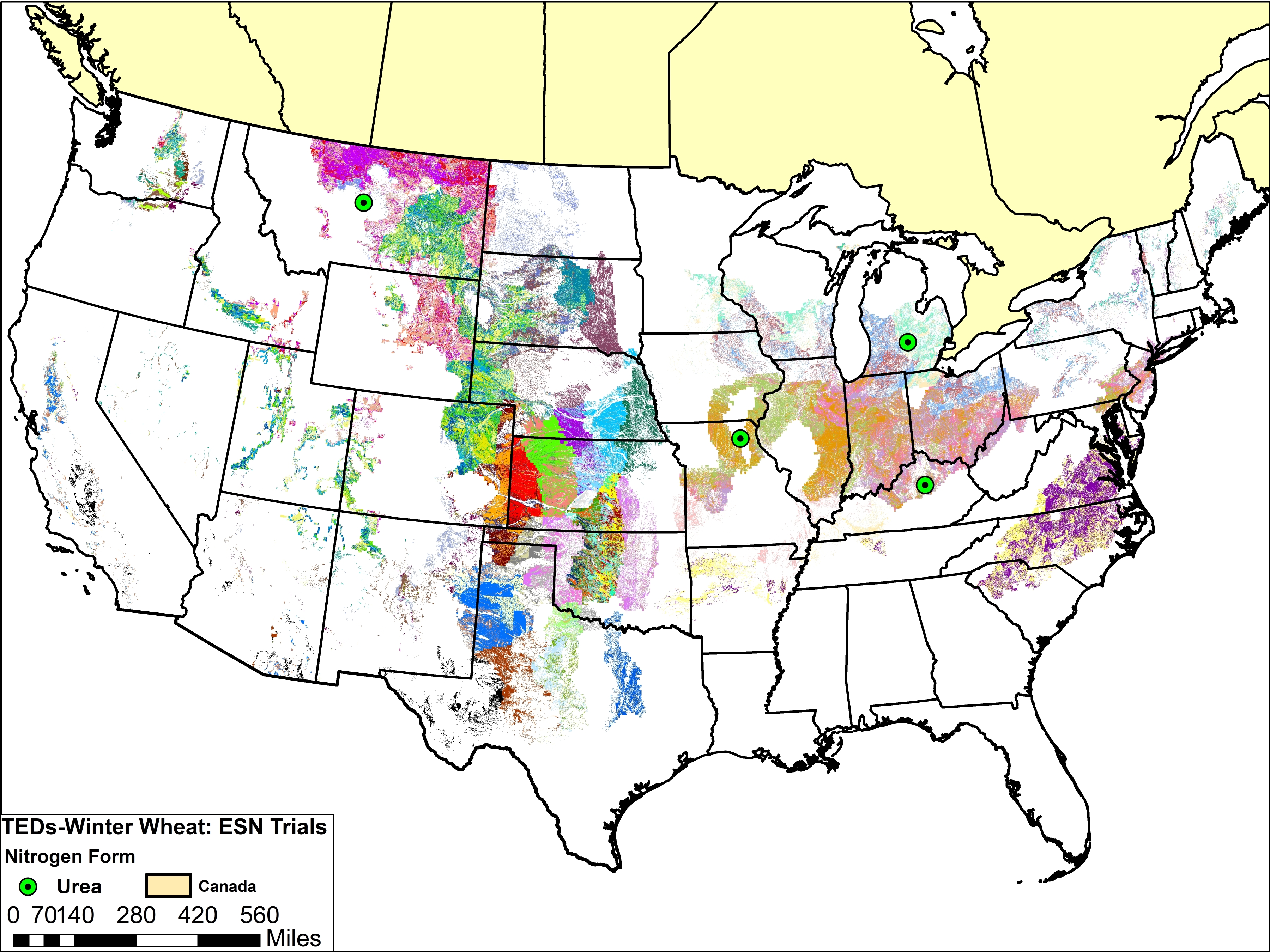
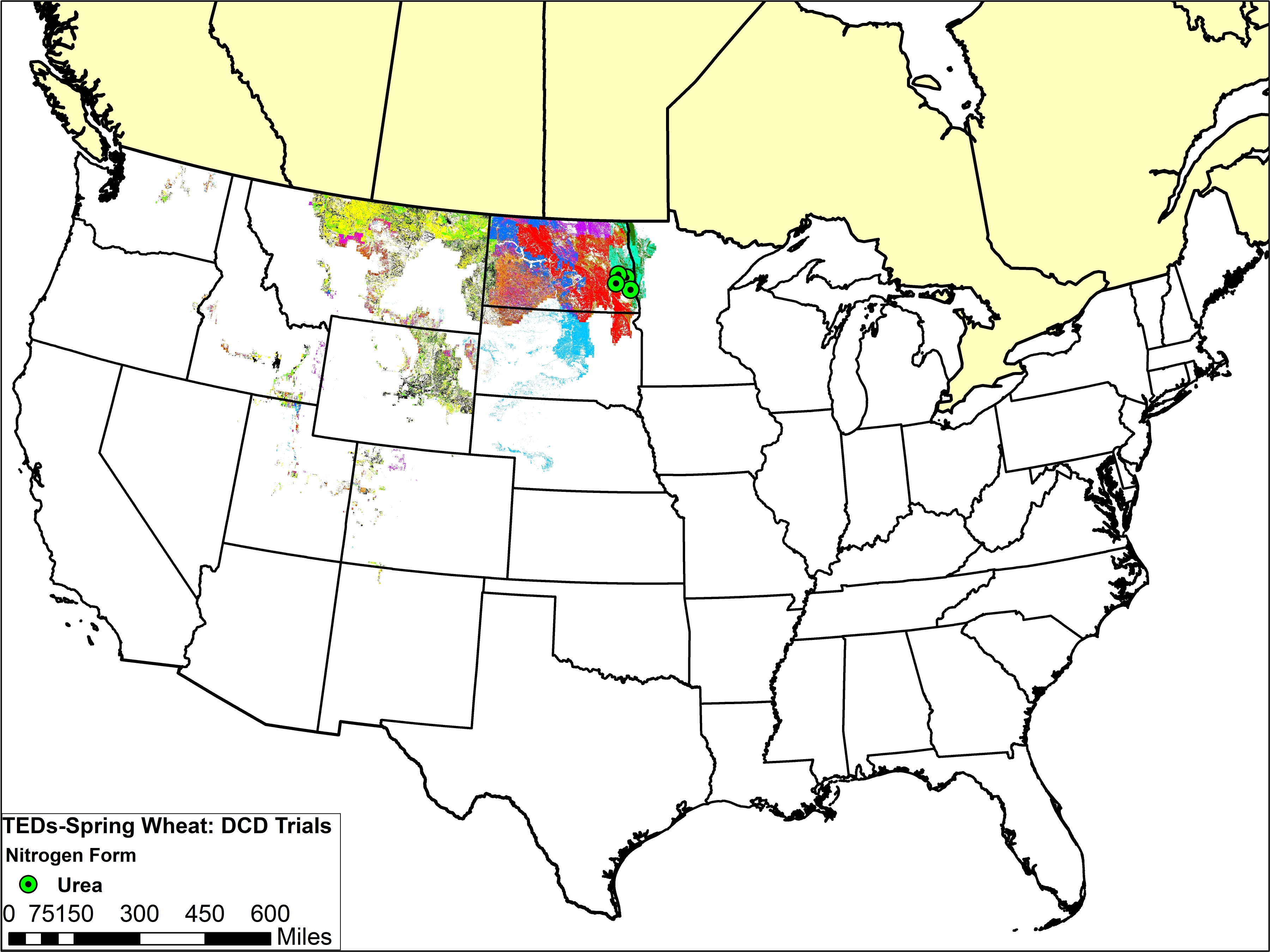
Dicyandiamide (DCD)
Dicyandiamide (DCD) is commonly used in fertilizer formulations as a nitrification inhibitor to slow the release of nitrogen (N) into plant available forms that are also more prone to losses.
DCD is an active ingredient in many mainstream enhanced-efficiency fertilizer products used in the U.S. including Guardian® products, Agrotain® Plus, and Super U®. The DCD in these products is intended to inhibit the activity of the Nitrosomonas bacteria, allowing for the stabilization of ammonium-N in the root zone, improving plants’ access to available nitrogen over the growing season. As a result, the addition of DCD has the potential to increase crop yields as well as reduce nitrogen loss through nitrification.
Depending on the specific product being used, DCD can be applied with either liquid or dry fertilizer, and is used with both inorganic fertilizer as well as liquid manure.
The maps below show trial locations for corn and wheat. The trial locations have been superimposed over the Technology Extrapolation Domains (TED) Framework. The TED Framework is described further on the DCD and TED Framework page.

With the data available, and in the conditions studied, DCD did not have any beneficial yield impacts for either wheat or corn. Some of the studies reporting yield decline may not have fully considered the potential for phytotoxicity with certain application methods. In addition, there are soil and climatic conditions under which DCD is expected to be more beneficial than others. Therefore, if DCD is to be recommended as a product for improving N use efficiency, more research (or increased accessibility of existing field data) is needed to determine the climate and soil characteristics or other management practices most likely to see such benefits.

To see if DCD trial locations are relevant to your operation, visit the DCD and TED Framework page.
To view the complete research report, including references, please visit the DCD Research Findings page.