SUPERU™
SUPERU™ is a self-contained granular fertilizer also intended to reduce ammonia volatilization and prevent nitrification, thus avoiding losses of ammonia to the air and nitrate to groundwater. It was available for on-farm use by the late 1990s and is made from a base of urea.
SUPERU™ includes both NBPT and DCD (as does AGROTAIN® PLUS). NBPT ((N-(n-butyl) thiophosphoric triamide) is a urease inhibitor. Dicyandiamide (DCD) is a nitrification inhibitor.
AGROTAIN®, AGROTAIN® PLUS, and SUPERU™ are related products manufactured and marketed by Koch Agronomic Services. All three products are sold to agricultural producers with the claim that they will improve nitrogen use efficiency and thus improve productivity. The expectation is that when N is limiting, effective urease and nitrification inhibitors will improve crop yield.
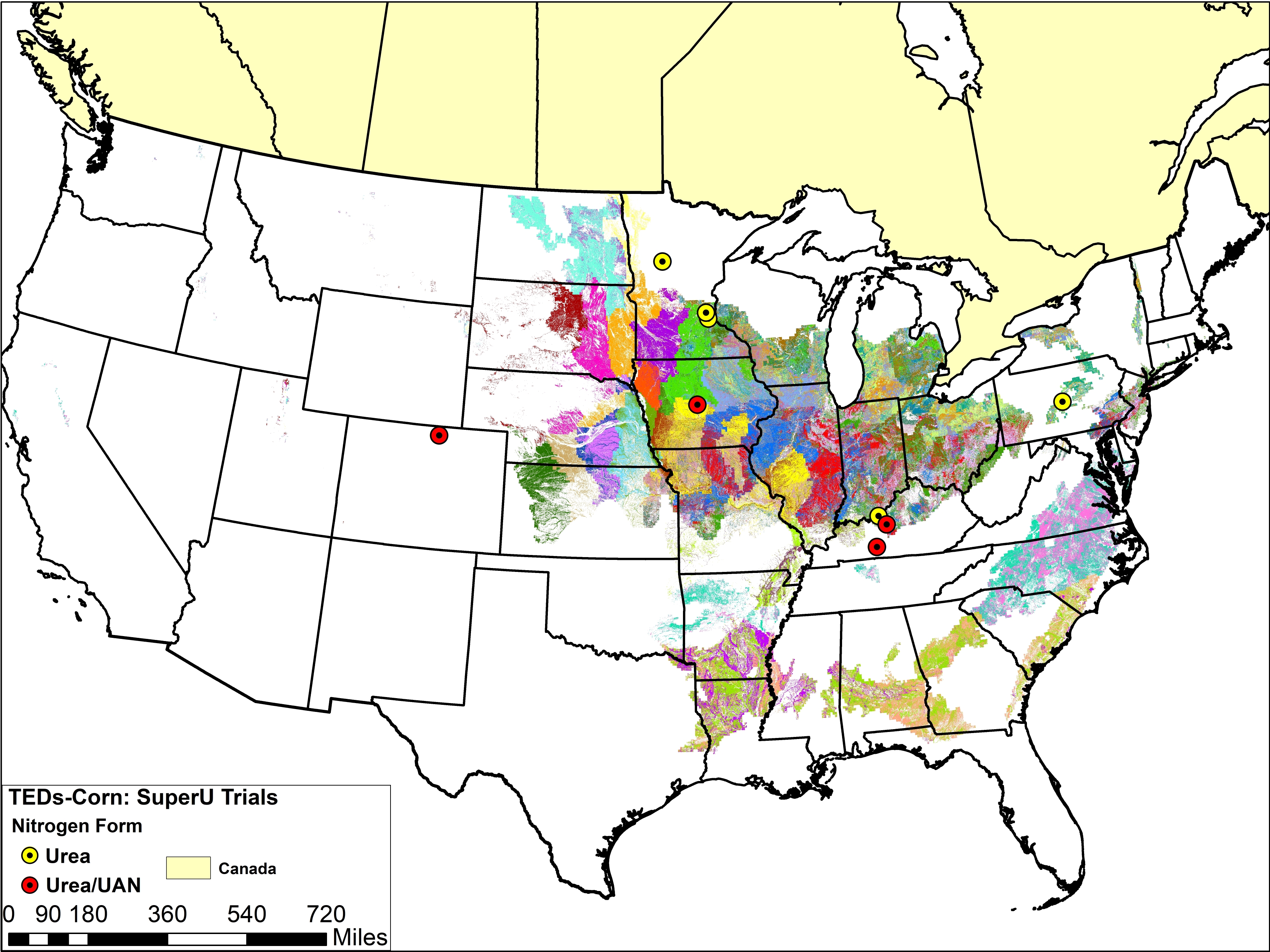
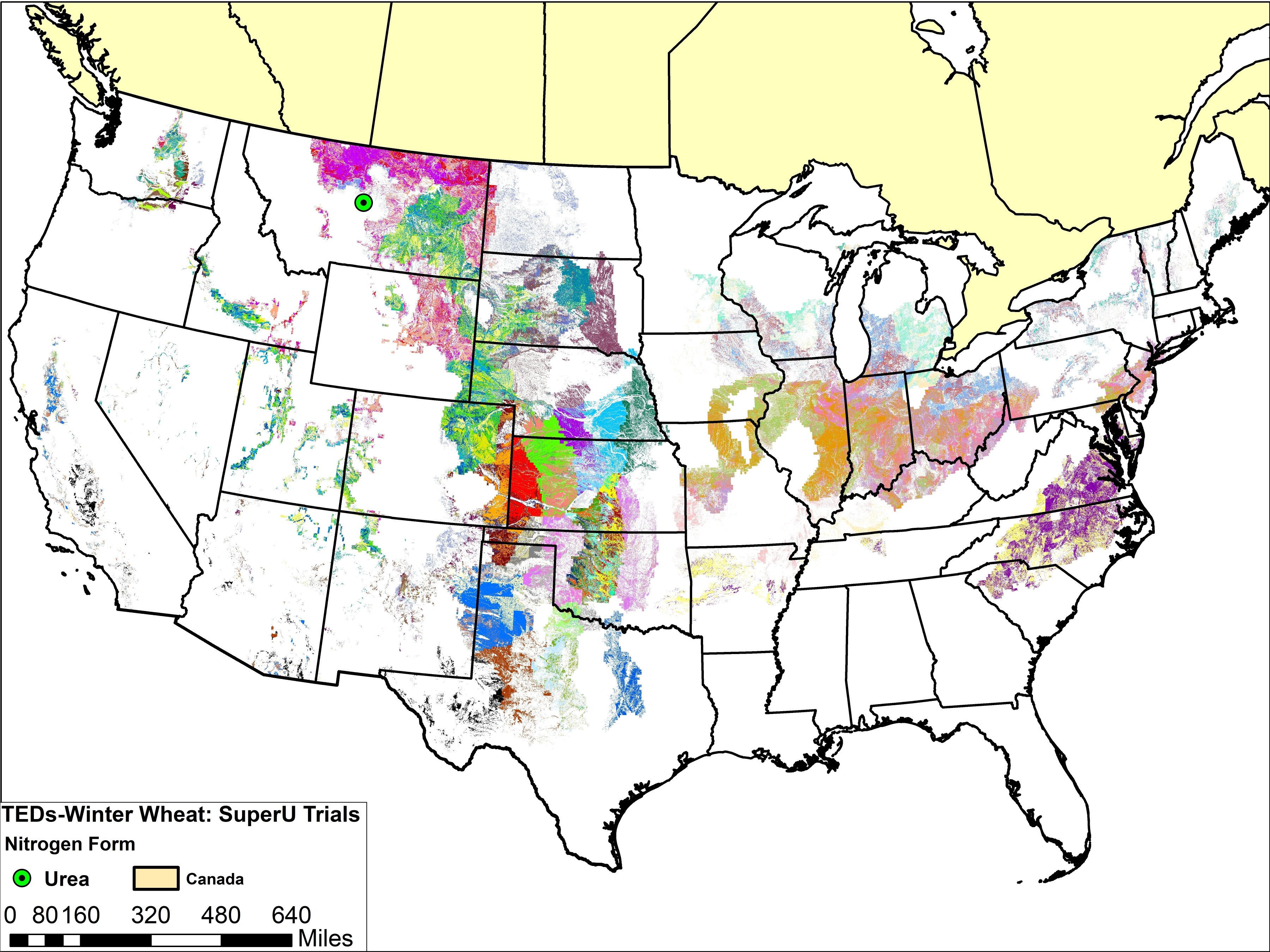
The maps below show trial locations for corn and wheat. The trial locations have been superimposed over the Technology Extrapolation Domains (TED) Framework. The TED Framework is described further on the SUPERU™ and TED Framework page.

When looking at yield effects only and keeping fertilizer rates constant, positive yield impacts for corn are evident for SUPERU™ (and AGROTAIN®), but the evidence is less compelling for AGROTAIN® PLUS. Limiting the analyses to peer-reviewed data reduces the effect size (in almost all cases) and reduces the statistical significance of positive impacts (primarily because of fewer observations).
There is no overall wheat yield response to SUPERU™.
The measured 22% lower yield-scaled N2O emissions from SUPERU™ compared with urea in corn systems represent significant improvements. A similar trend also seems possible for AGROTAIN® PLUS and SUPERU™ replacing UAN in corn systems. Therefore, while more data would of course be useful, these products do show some evidence of improving crop yield and reducing negative environmental impacts related to N losses.
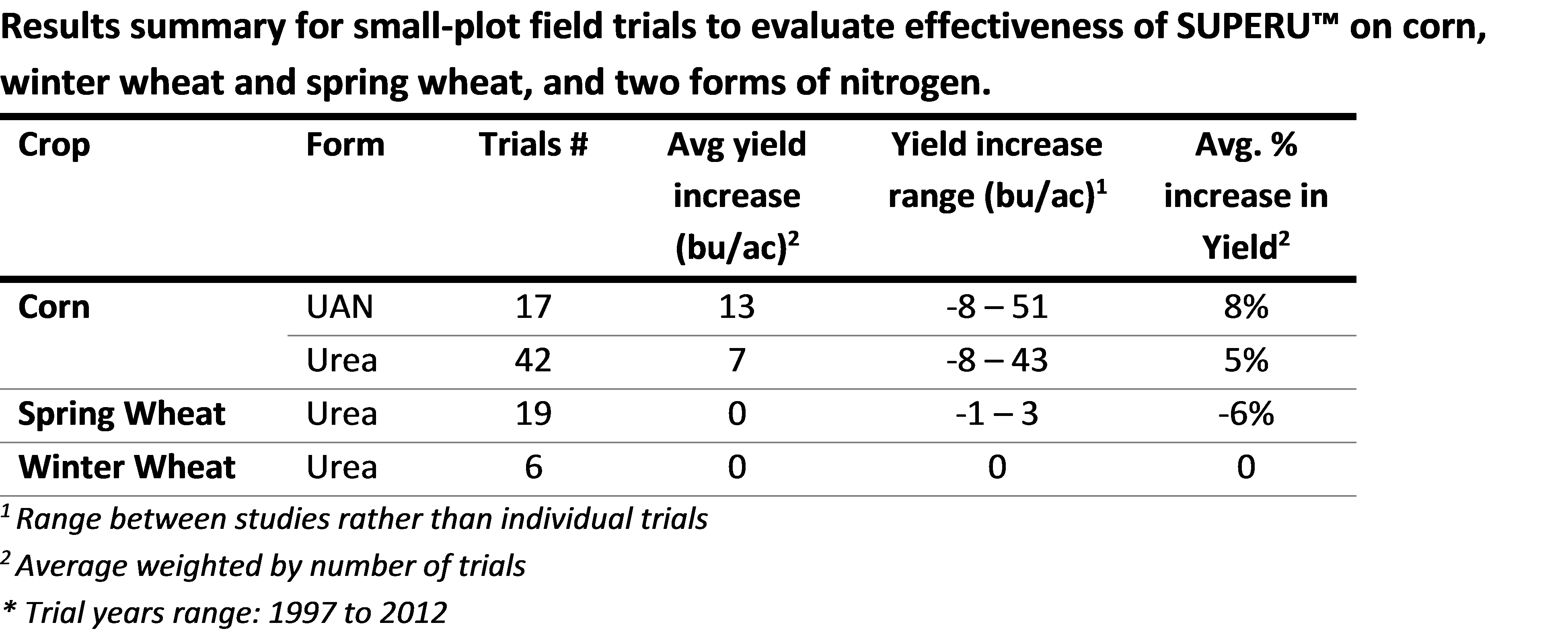
To see if SUPERU™ trial locations are relevant to your operation, visit the SUPERU™ and TED Framework page.
To view the complete research report, including references, please visit the SUPERU™ Research Findings page.